What are Networking in easy words?
Networking is the backbone of modern communication, enabling devices to connect and exchange data across local and global networks. At its core, networking involves the interconnection of devices, such as computers, smartphones, servers, and other hardware components, to facilitate the transmission of information. This transmission occurs through various protocols and technologies, creating a vast interconnected web that forms the foundation of the internet and other communication infrastructures.
Networking encompasses a wide range of concepts, technologies, and protocols, each serving specific purposes in facilitating communication between devices. At a fundamental level, networking involves the establishment, maintenance, and termination of connections between devices, enabling them to send and receive data packets efficiently and reliably.
The basic components of networking include:
Devices: Devices such as computers, routers, switches, servers, and mobile devices form the endpoints of a network. These devices are interconnected through physical or wireless connections, allowing them to communicate with each other.
Transmission Media: Transmission media refer to the physical pathways through which data travels between devices in a network. Common transmission media include copper cables, fiber-optic cables, and wireless signals.
Protocols: Protocols are sets of rules and conventions that govern how data is formatted, transmitted, received, and interpreted between devices in a network. Examples of networking protocols include TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), and DNS (Domain Name System).
Networking Hardware: Networking hardware includes devices such as routers, switches, modems, and network interface cards (NICs) that facilitate the routing, switching, and transmission of data within a network.
Networking Software: Networking software encompasses various applications, services, and operating system components that enable communication and network management tasks. Examples include network operating systems (e.g., Windows Server, Linux), network management tools, and communication protocols implemented in software.
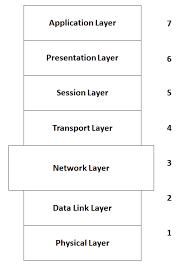
Layers of Networking:
Physical Layer: The physical layer is concerned with the transmission of raw binary data over the physical transmission medium. It defines specifications such as voltage levels, data rates, and connector types. Examples of physical layer technologies include Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and fiber optics.
Data Link Layer: The data link layer is responsible for the reliable transmission of data frames between adjacent nodes over a physical link. It handles tasks such as framing, error detection, and flow control. Ethernet, Wi-Fi (802.11), and PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) are examples of data link layer protocols.
Network Layer: The network layer is responsible for the routing and forwarding of data packets between different networks. It determines the optimal path for data transmission, manages network addressing, and handles logical addressing schemes. IP (Internet Protocol) is the primary network layer protocol in the TCP/IP model.
Transport Layer: The transport layer ensures reliable end-to-end communication between source and destination devices. It provides mechanisms for segmentation, reassembly, error recovery, and flow control. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are common transport layer protocols.
Session Layer: The session layer establishes, maintains, and terminates communication sessions between applications running on different devices. It handles session synchronization, checkpointing, and session recovery mechanisms.
Presentation Layer: The presentation layer is responsible for data translation, encryption, and compression to ensure that data exchanged between applications is in a usable format. It deals with data formatting, syntax conversion, and encryption/decryption.
Application Layer: The application layer provides network services directly to end-users and applications. It includes protocols and services such as HTTP, FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), and DNS (Domain Name System).
Networking technologies continue to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in hardware, software, and communication standards. Emerging technologies such as 5G wireless networks, software-defined networking (SDN), network virtualization, and Internet of Things (IoT) are reshaping the landscape of networking, enabling higher speeds, greater flexibility, and enhanced connectivity.
In conclusion, networking is a vast and essential field that underpins modern communication and connectivity. Understanding the principles, technologies, and protocols of networking is crucial for building and managing reliable, efficient, and secure network infrastructures. As technology continues to evolve, networking will remain a critical aspect of our increasingly interconnected world.
.png)


Comments
Post a Comment